Anxiety and fear are common emotions. But, while fear is a normal response to a perceived threat, anxiety is an unwarranted or inappropriate fear or response to a vague or ill-defined threat.
However, when these emotions are persistent, excessive and irrational, they may affect (a) the way a person leads his life, (b) the person’s ability to work and (c) the person’s ability to cope with the demands of life or relationships. When this happens, the anxiety becomes a disorder.
There are different types of anxiety disorders: phobia, generalised anxiety disorder, panic disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, acute stress disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
In Generalised Anxiety Disorder, however, the anxiety symptoms occurs most of the day, persistent and may not be restricted to any particular event.
Anxiety triggers unpleasant mental and physical symptoms such as feeling on edge; helplessness; repeated negative thoughts; confusion; worry; muscle tension; heart palpitations and/or difficulty breathing.
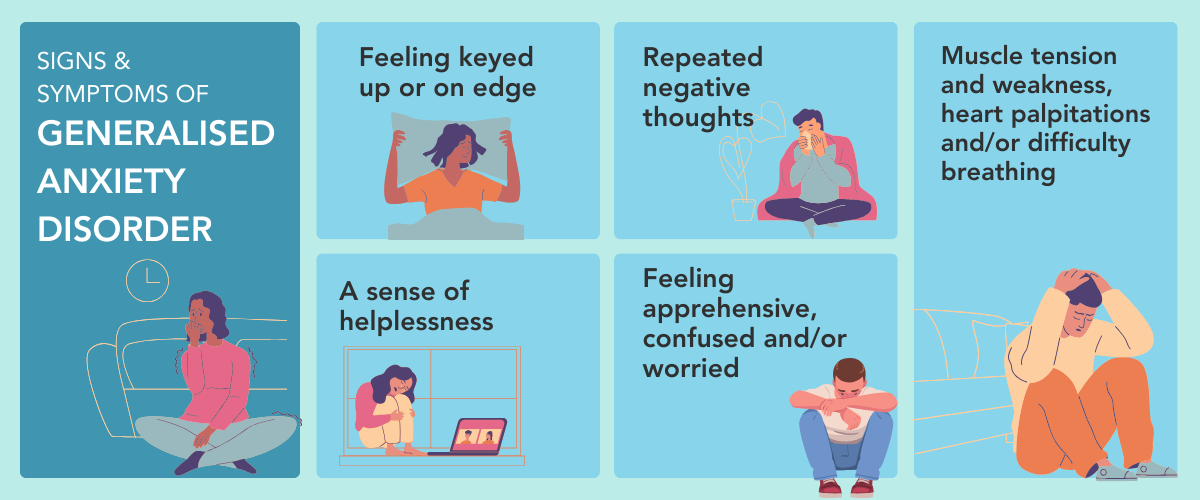
It is advisable to seek help as early as the symptoms are identified. A diagnosis needs to be made by a psychiatrist to ensure that there are no underlying medical conditions causing the symptoms.
There is usually a combination of factors that contribute to GAD. These may include a family history of a mental health condition, biochemical imbalances or excessive worries.
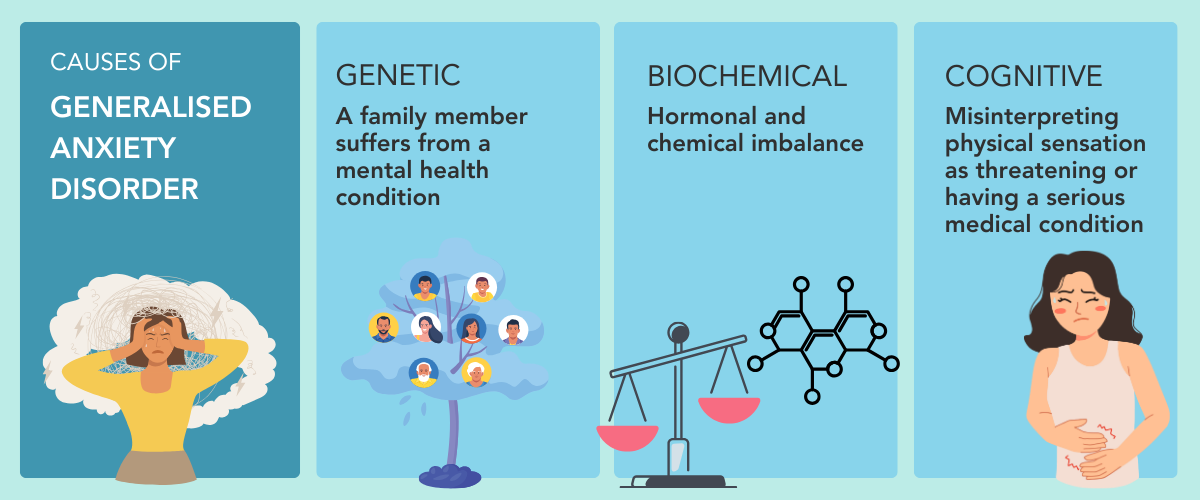
Early intervention will increase one’s chances of recovery. The aims of treatment are to reduce and eventually eliminate the signs and symptoms of anxiety disorders, and to restore quality of life. As GAD is considered a chronic illness, treatment options are generally for the long-term. These could include:
- Medications such as anti-depressants to help control anxiety — such medications have minimal side effects even with regular use. Sometimes, benzodiazepines can be used for short periods.
- Non-medication treatment options include cognitive methods, where patients are taught about the symptoms and bodily responses related to anxiety, and how to reframe thoughts. Behavioural methods may also be used, in which patients are exposed to possible triggers and taught relaxation techniques. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, changing one’s environment, could also help GAD patients, as excessive stress can trigger or worsen GAD.