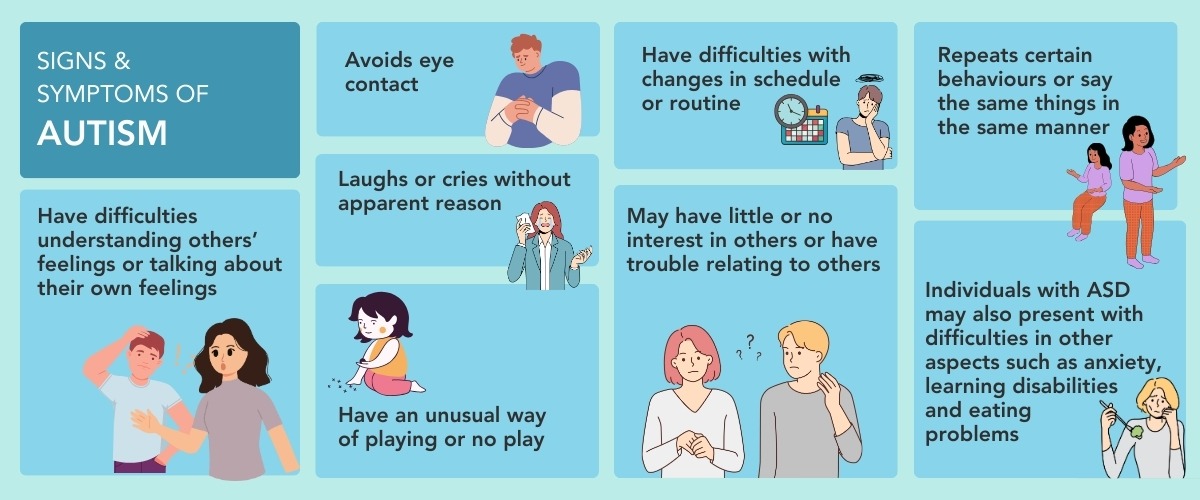
ASD looks different in each person, but children with ASD often face difficulty understanding the perspectives, emotions and non-verbal cues such as the body language of others. They may appear to ignore social cues and seem inflexible by doing things in specific ways. Learn more about the signs and symptoms of autism:
Difficulties in social communication
- Unable to reciprocate socially and emotionally: The child may have trouble maintaining conversations, expressing how they feel or sharing interests with others.
- Limited use of non-verbal communication during social interactions: The child may have difficulties making eye contact and using appropriate gestures. Their facial expressions and tone of voice may not match the social interaction.
- Difficulty establishing and sustaining relationships: It may be hard for the child to form friendships or maintain them, for instance.
- Trouble adjusting behaviour to different social context: The child might not understand unspoken social rules, like taking turns or being polite.
Pattern of repetitive behaviours and narrow interests
- Repetitive behaviours: The child may repeat words or phrases, movements, or use objects such as toys in a specific, repetitive manner.
- Constant need to keep to rigid routines and rituals: Small disruptions in routines may cause distress.
- Difficulty adjusting to change: Transitions or unexpected changes can be challenging.
- Highly restricted or focused interests: The child may become fixated on a particular topic, toy, activity, etc.
- Unusual reactions to sensory experiences: Some children may be hyper-sensitive to sensory inputs such as noise and sounds, while others may seem not to notice pain, heat or cold.
Dr Sung Min, Senior Consultant at the Department of Developmental Psychiatry, says that signs of ASD are typically observed in early childhood, around 4 to 5 years old, but can also be observed when the child is older.
 Many children with ASD struggle with how they take in and respond to sensory experiences. Sensory processing difficulties happen when the child has difficulty handling the sights, sounds, smells, textures or movements around them in the usual way, explains Ashley Jayapaul, Principal Occupational Therapist.
Many children with ASD struggle with how they take in and respond to sensory experiences. Sensory processing difficulties happen when the child has difficulty handling the sights, sounds, smells, textures or movements around them in the usual way, explains Ashley Jayapaul, Principal Occupational Therapist.
In fact, studies show that about 95 percent of children with ASD face some form of sensory processing difficulties. Some children can be extra sensitive to sensory input, avoiding it. Others may be less sensitive, requiring more sensory input when moving or coordinating their movements. These sensory differences can make daily activities more challenging.
When it gets too overwhelming, the child may feel anxious or stressed, and display certain behaviours to help them self-soothe. An example is stimming, or self-stimulating behaviour, which may include repetitive movements or sounds to help the child cope with sensory overload, stress, anxiety or even excitement.
According to Mr Jayapaul, sensory processing difficulties may look like:
- Covering ears in a noisy environment
- Avoiding crowded places
- Always touching things around them
- Jumping or seeking a lot of body movements
- Smelling or licking objects, walls or surroundings
There is currently no cure for autism. However, with the right intervention, education and support, children with ASD can show marked improvements in how they function and manage their challenges.
The goals in managing ASD, Dr Sung shares, is to facilitate normal development in the child's learning, language and social skills, while also reducing behaviours like rigidity, repetitive movements and hyperactivity.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach, and each management plan is tailored to each child and their caregivers.
Here's an overview of a range of therapies that support children with ASD, each delivered based on the individual's needs and at an age or developmentally appropriate level:
- Psychological Services: Some children with ASD may struggle with anxiety with routines change or when faced with unfamiliar social situations. Cognitive Behavioural Therapy may help them understand and manage their emotions. Social skills intervention programmes can also teach them how to read social cues and situations, respond appropriately and understand what behaviour is expected.
- Behavioural Therapy: Conducted by trained professionals, this type of therapy helps the child learn new ways of responding to situations. Typically, it focuses on modifying undesirable behaviour and reinforcing desirable ones in ways that are respectful, adopts natural consequences, and engages the child in their environment.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy helps individuals with ASD in handling their day-to-day activities. It may include sensory integration therapy to improve focus, coordination and emotional regulation; motor skills training, teaching handwriting skills, as well as life skills such as dressing, using utensils and feeding.
- Other interventions: Some children may benefit from Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) strategies, like the Picture Exchange Communication System (PECs) to support communication with others. Visual aids can also help children understand the daily tasks that they are expected to complete in school or at home.
- Medication: While there is no medication to cure autism, some may help manage conditions that may be more common in individuals with ASD. For instance, they may be used to alleviate hyperactive and disruptive behaviours that affect learning in schools. Note that medication is often used together with other therapies, and does not replace psychological intervention or behavioural management. Additionally, only certified doctors involved in autism care should prescribe medication.
Children with autism experience challenges in different ways, but learning how to support them at home can have a meaningful impact. Here, Mr Jayapaul shares some home-based strategies to manage the child's sensory processing difficulties.
For children who are easily overwhelmed, hypersensitive or avoidant of certain sensations:
- Keep the environment quiet and clutter-free
- Use visuals or schedules to help the child anticipate changes
- Allow more time for them to process instructions
- Play calming and predictable music such as nature sounds
For children who constantly seek sensory input:
- Give movement breaks, such as bouncing on a yoga ball or jumping on a trampoline before or during a table activity
- Offer safe sensory tools such as hand fidget toys, chewable pendants or necklaces, or textured teething-style toys
- Swimming may be helpful as the pressure of water and sensory experience can be calming for them
Overall, helping your child stay active can support their sensory needs and development. Simple "heavy work" activities - such as carrying groceries, cleaning windows, watering plants or moving furniture - are helpful. Regular outdoor play is just as important. Activities such as riding a bicycle, climbing playground ladders or slides, hanging on monkey bars, playing catch, skipping, hopscotch, provide movement input that many children with ASD need. Older children may also enjoy swimming and rock climbing.
While caring for a loved one with ASD can be deeply rewarding, caregivers and families also often face a long and demanding journey. This may place a heavy psychological burden on caregivers, which can worsen as they age, says Teo Ginnyueh, Head of Department of Medical Social Work at IMH.
Besides managing their child's condition, caregivers may also struggle with public stigma surrounding ASD. This can lead to caregiver burnout, isolation and a sense of being misunderstood.
Self-care - by looking after your body, mental health and relationships - can help caregivers stay resilient. Ms Teo suggests the following tips:
- Care for your body: Prioritise sleep, nutrition, regular exercise and medical check-ups. Even small acts like a haircut can lift mood.
- Stay connected: Nurture relationships with your spouse, family and friends.
- Make time for yourself: Take breaks or simply enjoy some quiet time alone.
- Know your limits: Accept that you don't have to do everything alone. Reach out for help or support.
- Acknowledge your emotions: Share your feelings with someone you trust or join a support group.
- Be mindful of how you appraise situations: How you view a situation affects how you cope. If you reframe a situation more positively, it helps you cope better.
- Empower yourself: Learn skills, discuss and work with educational and healthcare professionals to feel more confident in managing care.
- Celebrate the wins: Every progress or success - whether big or small - is worth celebrating.
Join the Autism Collaborative today!
If you're an individual with autism, a parent, caregiver or professional supporting the autism community, we invite you to be part of the Autism Collaborative. This is a Singapore-based initiative focused on enhancing support for individuals with ASD. It offers resources, training, and workshops for professionals and the autism community, aiming to promote awareness, research and partnerships in the field. Join us and stay updated on upcoming programmes at www.asdcollaborative.sg!
